On this page you will learn:
- About the overall architecture of the entire simulation platform
- About the code setup:
- of the Unity Client
- of the Server API
- of the Watchdog and the Simulations
For access to the actual source code, see the source code contributions page.
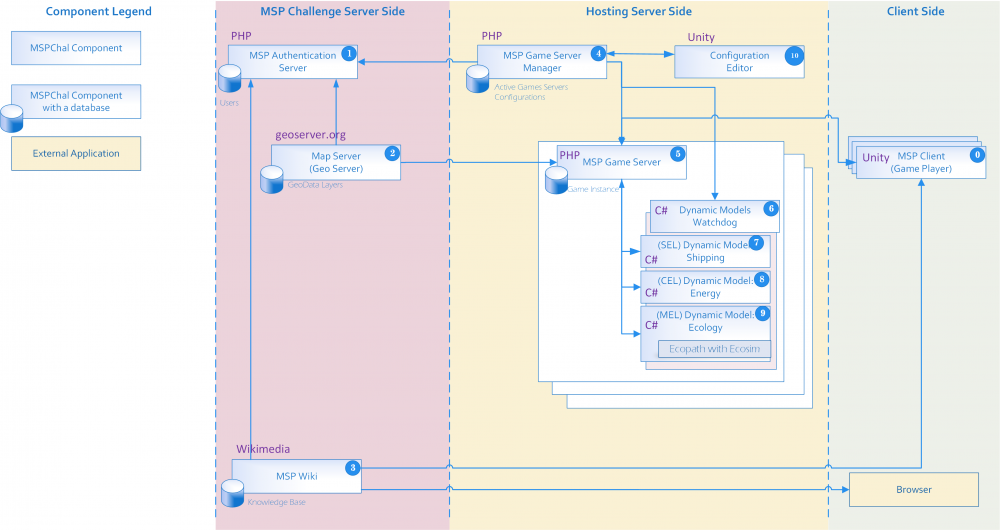
Overall architecture
The following diagram depicts the overall technical architecture of the MSP Challenge Simulation Platform.
The server consists of three main parts: the MSP Challenge server side (left), hosting server side (middle) and client side (right).
The MSP Challenge server side consists of three main components: an authentication server (1), a map server (2), and an MSP wiki (3). These server components take care of the underlying functions such as user and session authentication and the connection to a data server. This is needed to host, moderate and play an MSP Challenge session. At present Breda University of Applied Sciences hosts and maintains these components.
The hosting server side allows institutions to host MSP Challenge sessions on a central or local server. This entire part (4-10) is packaged in the full platform installer, available from the Download page.
The client (0) was built in a Unity game engine and links via a RESTFul API to the game server (5). The MSP Challenge client is the end-user’s main conduit to the entire platform. Changes to the world by the players are sent to the game server which then replicates to the other clients connected to the same server. The client takes care of rendering visual information and supports all user interactions. This includes viewing the sea basin world in its current and future state. Players can sketch, implement or archive plans. The results are calculated by the simulators but displayed in the client through performance graphs, such as increases or decreases in biomass, shipping route efficiencies, or energy production.
You can read much more about this architecture in the paper 'A Digital Game-based Simulation Platform for Integrated Maritime Spatial Planning: Design Challenges and Technical Innovations', published in 2020 by the Journal of Ocean Technology, and available from the Research Publications page.
More about the Unity client's setup and code
Getting started
- The MSP Challenge Client (0 in the diagram above) uses a specific Unity version. Check the Client column on the Release Notes page to see which version exactly.
- Clone the GitHub repository of the MSPChallenge-Client software to a local folder of your choice.
- Download and install the Unity Hub from unity.com.
- Within Unity Hub, download and install the version of Unity you need.
- Within Unity Hub, add the cloned MSPChallenge-Client folder on your computer as a Unity Project. Unity Hub should recognize the Unity version required.
- Open the Unity project by clicking on it in the Unity Hub. This will take a couple of minutes the first time. You'll probably get a warning to open in Safe Mode because of errors in the project. Open normally, not in Safe Mode. Once open, you'll see a bunch of errors in the Console. This is normal at this point, because you need additional plug-ins that we are not allowed to publish ourselves in a public Git repository.
- With the Unity editor open, download and install the following plug-ins:
- Download the Poly2Mesh ZIP file (which includes Poly2Tri) from here: https://luminaryapps.com/blog/triangulating-3d-polygons-in-unity/ Click the download link on the bottom of the page. Unzip the downloaded files in a new subfolder Poly2Mesh under the project's Assets > Plugins folder.
- Purchase, download and install the ODIN Inspector from here: https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/tools/utilities/odin-inspector-and-serializer-89041 Just follow the installation procedure offered.
- Purchase, download and install the Graph Maker from here: https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/tools/gui/graph-maker-11782 Again, just follow the installation procedure offered.
- Download the DOTween ZIP file from here: https://dotween.demigiant.com/download.php Important notes:
- Follow the installation and configuration steps from here: https://dotween.demigiant.com/getstarted.php
- The default modules as checked in the Setup DOTWeen... window are all you need. No need to select anything else, just continue.
- In the DOTween Utility Panel you'll also see a button to generate a .AMSDEF file. Do not push that.
- Close Unity. Re-open the Unity project from the Unity Hub.
- All errors (both during start-up and in the Console in the Unity editor itself) should now have disappeared.
- Open the NewLoginScene. Click the Play button in the top. Everything should now work. You are now ready to contribute.
Code notes
Server communications are done using the static ServerCommunication.cs class. In the very first session login screen the client communicates with the Server Manager API (see below). All server communication after that is with the server API directly, targeting a specific session that has already been set up on the server.
Practically all client-server communications goes through the Server.cs script. Here's an overview of all Server API endpoints called by the client.
More about the server's setup and code
ServerManager
The ServerManager is a separate PHP and jQuery web application running on the server's web address /ServerManager/. It has a back-end API with which the front-end HTML/CSS/jQuery end-user interface as well as the server API communicates.
The ServerManager API's structure follows the BREAD (Browse, Read, Edit, Add, Delete) actions that should be performed on the following objects:
- GameSession: the actual session to which MSP Challenge clients can connect, e.g. a North Sea edition instance.
- GameSave: a save of an actual session that can be reloaded or shared to others who can then import it into their own ServerManager.
- GameConfig: the configuration files with which MSP Challenge sessions can be created. Full documentation on the configuration data schema is available.
- GeoServer: instances of GeoServer containing appropriate vector or raster data layers that can be downloaded when creating a new session.
- Watchdog: instances of the Watchdog application (see also below) that control the simulations for each session.
- ServerManager: settings of the ServerManager application itself (e.g. its name, address, ...).
Server API
Underlying the ServerManager is a separate Server API. So this is a different PHP web application, and it runs on the server's root address. It listens to calls set up in the following manner:
http://[address]/[sessionID]/api/[class]/[method]
For example: http://localhost/1/api/plan/ExportPlansToJson
The sessionID refers to the actual MSP Challenge server session to which clients connect. Each session is set up in the aforementioned ServerManager.
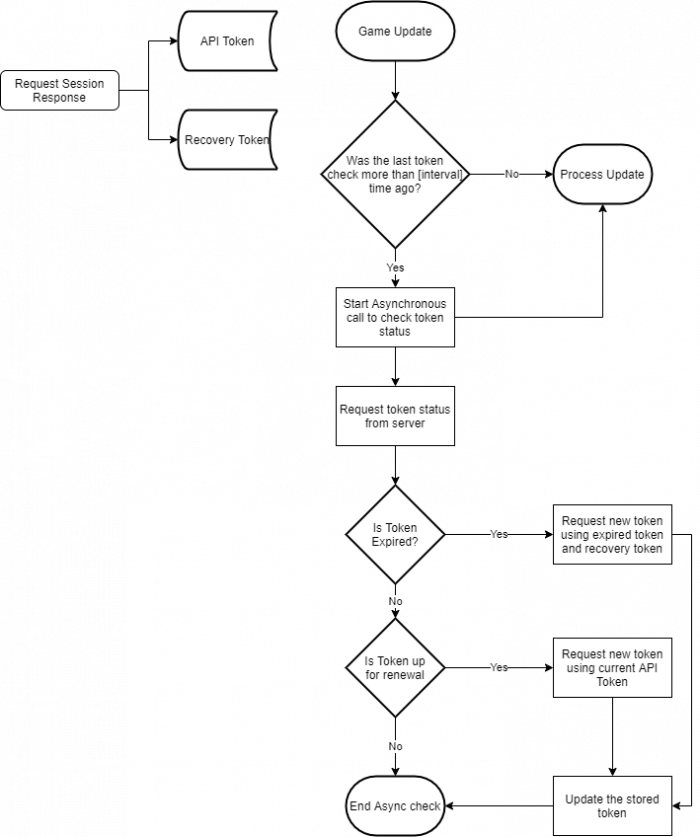
A security system guards whether specific server API calls are actually allowed. This system is based on those calling an API endpoint providing an MSPAPIToken in their header. In turn this token must of course first be requested from the server. The diagram below shows how this works out for the MSP Challenge Client:
Watchdog and Simulations
The Watchdog is a C# application that handles communications between the Server API on one end and the different simulations required for a specific MSP Challenge session on the other hand. So for example, it handles the energy, shipping and ecosystem simulations required for an instance of the North Sea edition. The Watchdog is again an API on a web server, waiting for requests to e.g. start a simulation executable, or push it to do another month of simulation. It can thus be set up on a different machine than the one running MSP Challenge Server.
More in-depth Docker services (MSP Challenge Server + hosting server side)
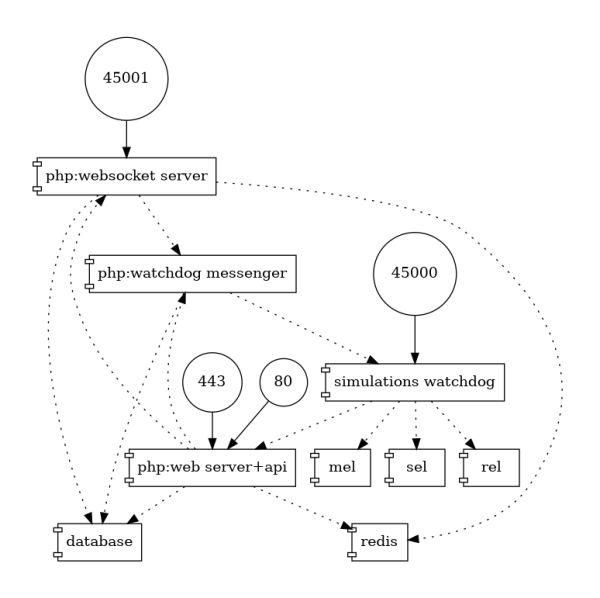
Running "MSP Challenge Server" on Docker will create multiple Docker containers, each having one or more services. It consistently under development - but this is how it looks in version 5.2.x on production:
| Container | Service/process | Exposed port(s) | Service software used | Docker image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| php | web service + api | 443 (https), 80 (http) | FrankenPHP based on Caddy | docker-hub.mspchallenge.info/cradlewebmaster/msp-challenge-server |
| web sockets | 443 (wss), 45001 (ws) | RatchedPHP | ||
| watchdog messenger | - | |||
| simulations | msw (watchdog) | 45000 (http) | .net6.0 application | docker-hub.mspchallenge.info/cradlewebmaster/msp-challenge-simulations |
| mel, sel, rel (simulations) | - | .net6.0 application | ||
| database | Relational database | unexposed | MariaDB | mariadb |
| redis | In-memory key-value database | unexposed | Redis | redis |
Of course any of these ports are customizable. The ones shown are the default values.
 Co-funded by the European Union.
Co-funded by the European Union.